Digital transformation has become a pivotal aspect of modern business strategies, intertwining environmental impact, technological trends, and sustainable practices. As companies navigate the evolving landscape of the digital economy, the need for a sustainable approach to digital transformation is more pressing than ever. This article delves into the intersection of digital transformation and sustainability, exploring key trends, challenges, and opportunities in this dynamic space.
Digital Transformation: A Sustainable Approach
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, the convergence of digital transformation and sustainability has emerged as a critical focus area for organizations looking to drive innovation, enhance operational efficiency, and address environmental concerns. The integration of sustainable practices into digital initiatives not only fosters responsible corporate citizenship but also unlocks new avenues for growth and competitiveness.
Introduction
Digital transformation is the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, resulting in fundamental changes to how companies operate and deliver value to customers. It is a critical strategy for companies that want to stay competitive in the digital age. The main drivers of digital transformation include:
- Technological advancements: The rapid pace of technological change requires businesses to adopt new technologies and processes to remain competitive.
- Customer expectations: Customers demand faster, more efficient, and personalized services, which can be achieved through digital transformation.
- Cost savings: Digital transformation can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved profitability.
Sustainability in Digital Transformation
Sustainability is an essential aspect of digital transformation, as it involves integrating sustainable practices into digital initiatives. The concept of sustainability in digital transformation includes:
- Environmental impact: Digital technologies can catalyze progress towards environmental goals but also pose risks like pollution and resource over consumption.
- Business strategies: Sustainable technology is crucial for contemporary businesses, enabling them to create new models and enhance customer experiences.
- Technology trends: Embracing Industry 4.0 as a key element for digital transformation is essential for sustainable outcomes.
Objectives
The main objective of this article is to explore the intersection of digital transformation and sustainability, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities in this dynamic space. The article aims to provide insights into the importance of sustainability in digital transformation and offer an overview of the topic, including its main themes and benefits.
Environmental Impact of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation has both positive and negative environmental impacts. On one hand, it can improve efficiency and productivity across sectors, reducing carbon emissions in agriculture, transport, planning, waste management, and public services. On the other hand, the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with digital technologies are significant.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions
- Data Centers: Data centers account for 45% of greenhouse gas emissions in the global ICT sector.
- Electronic Devices: The manufacturing, shipping, and powering of digital devices consume a vast amount of energy and contribute to land quality degradation and biodiversity loss.
- Digital Communication: Sending one email emits around 4g of CO2, and a typical user of a business email account emits around 135kg of CO2 annually.
- Internet Browsing: Internet browsing accounts for a significant portion of digital carbon emissions.
- Video and Music Streaming: These activities are among the biggest contributors to the digital carbon footprint due to the energy needed to run devices and power servers.
Waste Generation and Resource Depletion
- E-Waste: The waste management sector operates with low margins and is highly competitive, continuously under pressure to reduce costs. Digital technologies require investment but offer scalable efficiencies4.
- Material Use: The production of infrastructure, computing machines, and other elements required for digital technologies has a direct impact on land quality and biodiversity.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Energy Efficiency: Sustained gains in energy efficiency could keep overall energy demand growth largely in check for data centers and networks.
- Digital Analytics: Reducing O&M costs, enabling predictive maintenance, and lowering costs for the owner of plants and networks can ultimately save consumers money.
- Smart Demand Response: This could provide 185 GW of system flexibility, roughly equivalent to the currently installed electricity supply capacity of Australia and Italy combined, saving USD 270 billion of investment in new electricity infrastructure.
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Digitalization can help integrate variable renewables by enabling grids to better match energy demand to times when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing.
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Rolling out smart charging technologies for electric vehicles could help shift charging to periods when electricity demand is lower, providing further flexibility to the grid while saving between USD 100 billion and USD 280 billion (depending on the scenario).
- Distributed Energy Resources: Digitalization can facilitate the development of distributed energy resources, such as household solar PV.
Digital transformation has both positive and negative environmental impacts. While it can improve efficiency and reduce carbon emissions, the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with digital technologies are significant.
To mitigate these impacts, it is crucial to focus on energy efficiency, digital analytics, smart demand response, integration of renewable energy sources, electric vehicle charging, and distributed energy resources.
What are some examples of sustainable digital transformation practices in the energy sector?
Some examples of sustainable digital transformation practices in the energy sector include:
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: Companies are increasingly leveraging digital technologies to integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into their energy production processes. This shift towards renewable energy helps reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
- Smart Grids and IoT: Implementing smart grids and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies allows for more efficient energy distribution, real-time monitoring, and optimization of energy consumption. These technologies enable better management of energy resources and contribute to overall sustainability efforts.
- Data Analytics for Energy Efficiency: Utilizing data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics in the energy sector helps companies optimize energy usage, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency. By analyzing data, companies can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce energy waste.
- Cloud Computing Applications: Cloud computing applications play a significant role in managing energy production, distribution, and provision efficiently. These applications enhance collaboration, provide real-time insights to customers, and support predictive maintenance of energy assets, ultimately contributing to sustainability efforts.
- Blockchain Technology for Energy Trading: Blockchain technology is being used to facilitate transparent and efficient energy trading, track the source of renewable energy, and automate transactions between buyers and sellers of excess energy. This technology enhances trust, security, and transparency in energy transactions while promoting sustainability.
These sustainable digital transformation practices in the energy sector demonstrate how companies are leveraging technology to improve efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, optimize energy usage, and enhance overall sustainability in their operations.
PCODE : HA1
Social Impact of Digital Transformation

Digital transformation has a significant social impact, influencing various aspects of society. Key areas affected include data privacy, digital inclusion, digital literacy, and digital well-being.
Data Privacy
- Data Security: Digital transformation raises concerns about data security and privacy, as the collection and storage of personal information increase.
- Cybersecurity: With the growing digital landscape, cybersecurity becomes crucial to protect sensitive data from cyber threats.
A Digital Inclusion
- Access to Technology: Digital transformation can bridge the digital divide by providing access to technology and online resources for marginalized communities.
- Skills Development: Enhancing digital literacy skills among individuals ensures inclusivity in the digital era.
Digital Literacy
- Education: Digital transformation necessitates a focus on educating individuals on how to effectively use digital technologies for personal and professional growth.
- Training Programs: Offering training programs can empower individuals to navigate the digital landscape with confidence.
The Digital Well-being
- Mental Health: Excessive use of digital technologies can impact mental health, emphasizing the need for promoting digital well-being .
- Work-Life Balance: Digital transformation can blur boundaries between work and personal life, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy balance.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Digital Divide: Addressing disparities in access to technology and internet connectivity is crucial for ensuring digital inclusion3.
- Privacy Regulations: Implementing robust data privacy regulations and cybersecurity measures is essential to protecting individuals’ data in the digital age.
- Education and Training: Investing in digital literacy programs and training initiatives can empower individuals to leverage technology effectively.
- Promoting Well-being: Developing strategies to promote digital well-being, such as setting boundaries on technology use and fostering a healthy relationship with digital tools, is vital for societal health.
In conclusion, the social impact of digital transformation encompasses data privacy concerns, efforts towards digital inclusion, the importance of enhancing digital literacy, and promoting digital well-being. Addressing challenges related to data security, access to technology, education, and well-being presents opportunities for societies to harness the benefits of digital transformation while mitigating its risks.
What are some examples of digital technologies that have improved data privacy?
Some examples of digital technologies that have improved data privacy include:
- Homomorphic Encryption: This technology enables computational operations on encrypted data, ensuring that the results of any analysis remain encrypted and only the data owner can decrypt and view them. It allows companies to analyze encrypted data in cloud storage or share sensitive data securely1.
- Secure Multiparty Computation (SMPC): SMPC is a sub-field of homomorphic encryption that distributes computation across systems and multiple encrypted data sources. This technique ensures that no party can see the entire data set, enhancing privacy and limiting the information any party can access.
- Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP): ZKP is a set of crypto-graphic algorithms that enable information to be validated without revealing the underlying data. It plays a crucial role in identity authentication, allowing for verification without disclosing sensitive information.
- Tokenization: Tokenization involves substituting sensitive data like credit card numbers with randomly generated tokens. The mapping of tokens to original data is stored securely, and there is no mathematical relationship between the token and its original data, enhancing security and privacy.
- Data Access Governance: This technology provides visibility into where sensitive data exists, who has access to it, and their activities. It helps organizations manage data access permissions effectively, identify stale data, and automate data protection processes.
- Consent/Data Subject Rights Management: Tools for managing consent of customers and employees, enforcing their rights over personal data, and enabling organizations to search, identify, segment, and amend personal data as needed. These tools help ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR.
These technologies play a crucial role in enhancing data privacy by encrypting sensitive information, securing access to data, managing consent effectively, and enabling organizations to protect personal data while extracting value from it.
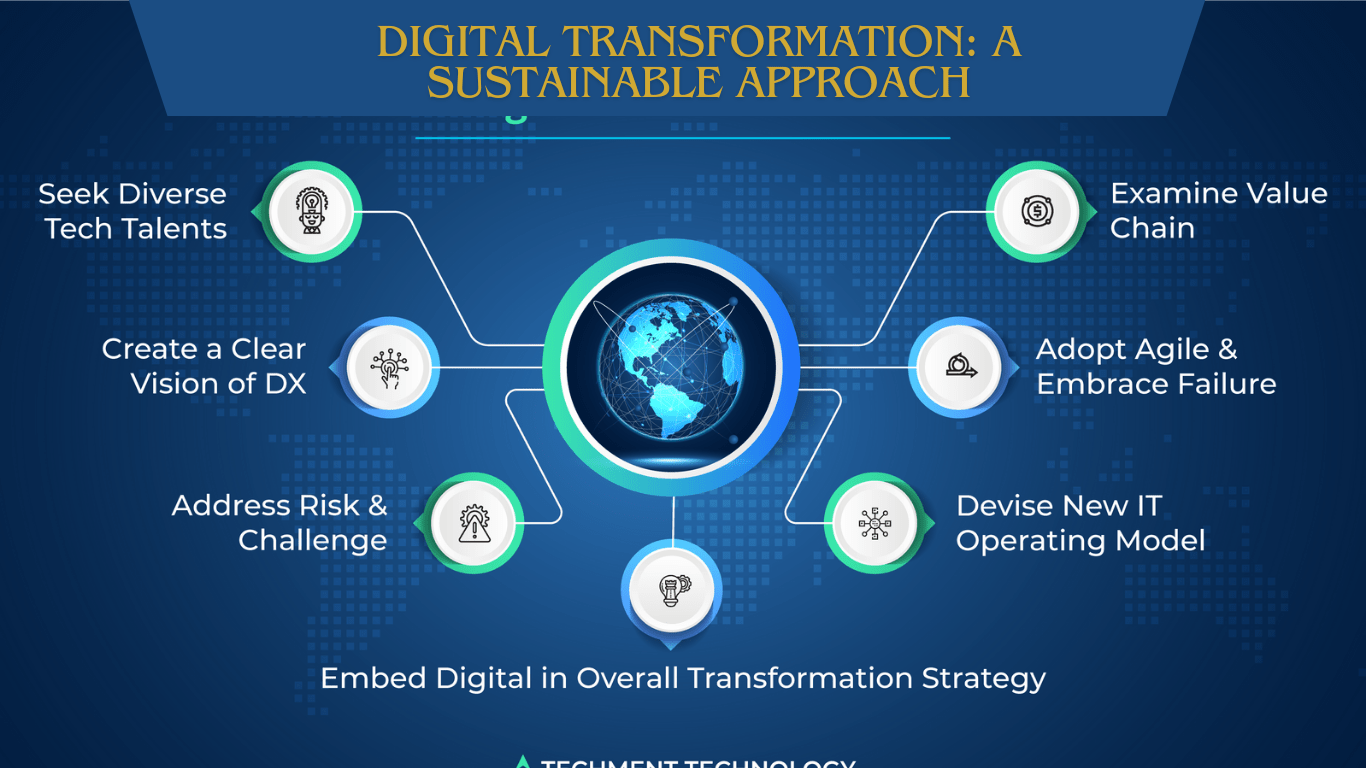
Best Practices for a Sustainable Digital Transformation
a. Green IT
Green IT involves the use of digital technologies to reduce the environmental impact of IT operations. This includes energy-efficient hardware, data center optimization, and the use of renewable energy sources for powering IT infrastructure.
b. Circular Economy
A circular economy aims to eliminate waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use, and regenerate natural systems. In the context of digital transformation, this can be achieved by designing products and services with sustainability in mind, using renewable energy, and implementing circular business models.
c. Digital Ethics
Digital ethics involves the responsible use of digital technologies, ensuring privacy, security, and transparency. This includes data protection, responsible data sharing, and the development of ethical AI systems.
d. Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, is crucial for a sustainable digital transformation. This involves communicating the benefits of sustainability, gathering feedback, and collaborating on sustainable solutions.
Case Studies
- Google: Google has implemented a sustainable digital transformation strategy, focusing on renewable energy, energy-efficient data centers, and sustainable product design. The company has also invested in renewable energy projects and aims to be carbon-neutral by 2030.
- Microsoft: Microsoft has committed to being carbon-negative by 2030 and has implemented a circular economy strategy for its products. The company has also invested in renewable energy and energy-efficient data centers.
- IBM: IBM has a sustainability strategy that includes reducing its carbon footprint, promoting renewable energy, and investing in sustainable technologies. The company has also implemented a circular economy strategy for its products.
- Amazon: Amazon has a sustainability strategy that includes reducing its carbon footprint, promoting renewable energy, and investing in sustainable technologies. The company has also implemented a circular economy strategy for its products.
- Siemens: Siemens has a sustainability strategy that includes reducing its carbon footprint, promoting renewable energy, and investing in sustainable technologies. The company has also implemented a circular economy strategy for its products.