
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet, offering on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable resources, such as networks, servers, storage, applications, and services. This transformative technology has become ubiquitous, enabling businesses to scale, innovate, and reduce costs. The benefits of cloud computing include reduced capital expenses, scalability, flexibility, and improved collaboration.
However, challenges such as security concerns, downtime, and internet connection dependency should be carefully considered. This article provides a comprehensive guide to cloud computing, covering its definition, characteristics, benefits, challenges, and an overview of the content and main objectives.
Introduction:
Cloud computing, a revolutionary concept, provides on-demand access to a shared pool of resources over the internet, offering businesses unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand self-services
- Broad network access
- Rapid elasticity
- Resource pooling
- Measured service
- Multi-tenancy
- Virtualization
- Resilient computing
- Flexible pricing models
- Security
- Automation
- Sustainability.
- Reduced capital expenses
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Cost savings
- Better collaboration
- Business continuity
- Performance
- Reliability
- Security
- Automation
- Sustainability
Challenges of Cloud Computing:
- Security concerns
- Downtime
- Internet connection dependency
- Data governance
- Configuration errors
- Lack of security patches
- Vendor lock-in
- Integration complexity
- Unforeseen costs.
what are the main characteristics of cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that provides on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable resources, such as networks, servers, storage, applications, and services over the internet.
The main characteristics of cloud computing are:
- On-demand self-services: Cloud users can provision computing capabilities like server time, network storage, applications, etc. automatically as needed without requiring human interaction with the service provider.
- Broad network access: Data can be uploaded and accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. Users can work from any location.
- Resource pooling: Resource pooling means a cloud service provider can share resources among several clients, providing everyone with a different set of services per their requirements. It is a multi-client strategy that can be applied to data storage, processing, and bandwidth-provided services.
- Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released to scale rapidly based on demand. This supports the ability to scale up or down resources like storage, computing power, etc. automatically.
- Measured service: Cloud computing employs a usage-based or pay-per-use billing model. Resource usage is monitored, measured, and reported transparently for billing as per usage metrics like storage consumed, bandwidth utilized, active user accounts, etc.
- Multi-tenancy: Multiple customers share the same physical infrastructure. This means that different companies’ data is stored separately, but they all have access to the same services.
- Virtualization: The ability to run multiple operating systems on a single server. This can be done by using virtual machines, which are software that allows you to run an entire operating system on a single machine.
- Resilient computing: The ability for your data to be resilient in the event of a failure or to be available when it’s needed. This can be accomplished through redundancy and failover features.
- Flexible pricing models: Cloud computing characteristic allows businesses to use resources as they need them instead of paying for storage space that may go unused. This is one of the many effective cloud computing features.
- Security: Cloud computing features provide security by using multiple layers of protection, including firewalls, encryption, and identity management systems. It provides enhanced security for your business data and applications by leveraging standard practices in information.
Types of Cloud Computing Services?

The three main types of cloud computing services are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each type offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management, catering to various business needs.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers the fundamental building blocks for IT, such as virtual servers, storage, and networking. Users can rent these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing for scalability and flexibility. Examples of IaaS include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine.
Advantages:
- Flexibility and scalability
- Cost-effective, pay-as-you-go model
- Reduced need for on-premises hardware
Disadvantages:
- Requires more management and technical expertise
- Potential security concerns due to user-managed infrastructure
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure. It typically includes development tools, database management, and application hosting. Examples of PaaS include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Microsoft Azure, and Google App Engine.
Advantages:
- Streamlined application development
- Reduced infrastructure management
- Automatic scaling and backup
Disadvantages:
- Less control over underlying infrastructure
- Limited to the platform’s features and tools
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the software through a web browser, and the provider manages everything, from the infrastructure to the application itself. Examples of SaaS include Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft 365.
Advantages:
- Easy accessibility and maintenance
- Automatic updates and patches
- Scalability and customizability
Disadvantages:
- Limited customization options
- Data security and privacy concerns.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different business requirements. IaaS provides the most control and flexibility, PaaS streamlines application development, and SaaS offers ready-to-use software with minimal maintenance. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their cloud computing needs.
What are the advantages of using iaas for businesses?
The advantages of using Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) for businesses are as follows:
- Cost Reduction: IaaS reduces costs by eliminating the need to purchase and maintain physical hardware. It operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale operations as needed without incurring significant upfront expenses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: IaaS promotes scalability and flexibility, enabling businesses to quickly expand or contract their IT infrastructure based on demand. This is particularly beneficial for companies experiencing rapid growth or fluctuations in resource requirements.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: IaaS supports disaster recovery and business continuity by providing resilient computing resources. This ensures that businesses can maintain operations even in the event of a system failure or a catastrophic event.
- Freedom to Onboard New Employees and Support Remote Work: IaaS allows businesses to onboard new employees quickly and provide them with the necessary IT resources, regardless of their location. This is especially advantageous for companies with remote workers or those operating across different geographical locations.
- Tighter Security: Many IaaS providers offer robust security measures, focusing on providing a secure computing environment. This can help businesses enhance their overall security posture and protect their data and applications.
- Focus on Business Growth: By offloading infrastructure management to an IaaS provider, businesses can free up their internal resources to focus on core business activities and innovation, thus driving business growth.
IaaS offers several advantages for businesses, including cost reduction, scalability, disaster recovery support, flexibility, security, and the ability to focus on business growth. These benefits make IaaS a compelling option for organizations looking to modernize their IT infrastructure and optimize their operations.
What are some examples of iaas providers?
Some examples of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a wide range of IaaS services, including Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) and Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3).
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure provides IaaS solutions, allowing users to deploy and manage virtual machines, containers, and other infrastructure components.
- Google Cloud: Google Cloud Platform offers IaaS services such as Compute Engine, which provides virtual machines for running large-scale workloads2.
- IBM Cloud: IBM’s IaaS offerings include virtual servers, storage, and networking resources, enabling businesses to build and deploy a wide range of applications.
- Alibaba Cloud: Alibaba’s Elastic Compute Service (ECS) is a prominent IaaS solution, providing scalable computing resources for businesses.
These providers offer a variety of infrastructure services, allowing organizations to outsource their IT infrastructure and access computing resources over the internet.
Types of Cloud Computing Deployment Models?
Four main types of cloud deployment models are:
- Public Cloud
- Offers shared infrastructure and resources over the internet.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Private Cloud
- Dedicated to a single organization, providing a high level of security and control.
- Examples: On-premises data centers, software-only private clouds (OpenStack), hardware-and-software private clouds (HPE GreenLake)
- Hybrid Cloud
- Combines public and private clouds, allowing organizations to orchestrate workloads across both environments.
- Examples: AWS Outposts, Azure Stack, Azure Arc, Azure VMware Solution, Google Anthos
- Community Cloud
- Shares resources and services among organizations with common business requirements.
- Examples: Organizations in the same industry or departments of the same organizational body
Advantages and disadvantages of each type are as follows:
Public Cloud
a. Advantages:
- Low cost
- Scalability
- High availability
- No need for infrastructure management
b. Disadvantages:
- Less secure
- Limited customization
Private Cloud
a. Advantages:
- High security
- High performance
- Customization
b. Disadvantages:
- Higher cost
- Requires infrastructure management
Hybrid Cloud
a. Advantages:
- Flexibility
- Cost management
- Agility and scalability
b. Disadvantages:
- Complexity
- Security concerns
Community Cloud
a. Advantages:
- Cost savings
- Shared resources and services
- Compliance with industry regulations
b. Disadvantages:
What are some examples of public cloud providers?
Some examples of public cloud providers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Offers a wide range of cloud services, including computing power, storage options, and networking.
- Provides services such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS).
- Microsoft Azure
- Provides a variety of cloud services, including computing, analytics, storage, and networking.
- Offers services such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure SQL Database.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Offers cloud computing services, including data storage, data analytics, and machine learning.
- Provides services such as Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, and Google BigQuery.
- IBM Cloud
- Offers a range of cloud computing services, including infrastructure, platform, and software services.
- Provides services such as IBM Virtual Servers, IBM Cloud Object Storage, and IBM Db2 on Cloud.
These public cloud providers offer a variety of services and are known for their scalability, flexibility, and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Cloud Computing Trends and Applications?
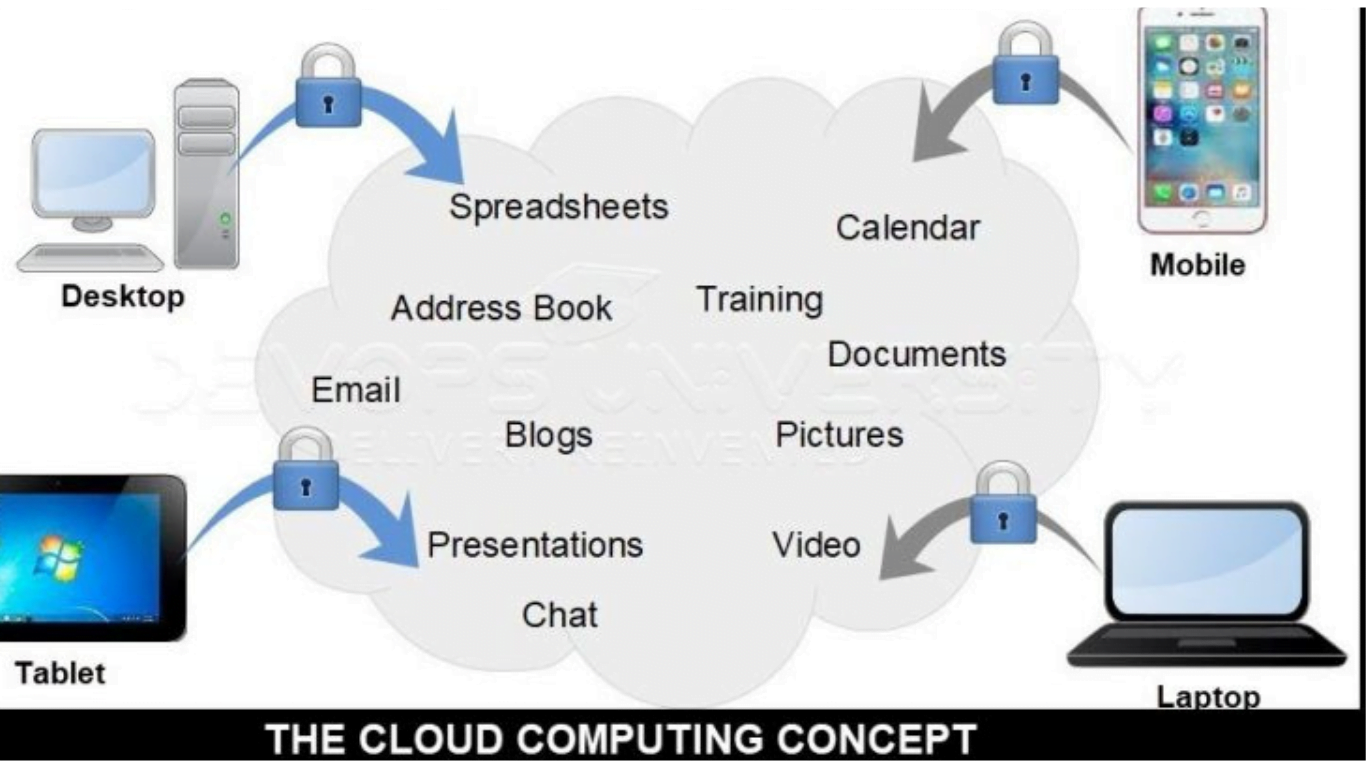
Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving technology that is transforming the way businesses operate. Some of the current and future trends in cloud computing include:
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is a framework in which data is stored and processed as close to the original device as possible. This reduces latency and bandwidth requirements, enabling faster and more efficient data processing.
- Server-less Computing: Server-less computing is an emerging trend in cloud computing that allows developers to run code without managing servers. This approach can reduce infrastructure costs and increase scalability.
- Artificial Intelligence: Cloud infrastructure has a big role to play in making AI available to the masses, along with all the economic and social benefits that it’s expected to generate. AI-as-a-service through cloud platforms is becoming more accessible to businesses.
- Blockchain: Block-chain is a distributed ledger technology that is being integrated with cloud computing to create new applications and services.
Cloud computing is being used in various industries and domains, such as healthcare, education, finance, and entertainment. Some examples of how cloud computing is used in these industries are:
- Healthcare: Cloud computing is used to store and manage electronic health records, enabling healthcare providers to access patient data from anywhere, at any time. It also facilitates telemedicine, allowing doctors to diagnose and treat patients remotely.
- Education: Cloud computing is used to provide online learning platforms, enabling students to access educational resources from anywhere, at any time. It also facilitates collaboration between students and teachers.
- Finance: Cloud computing is used to provide financial services, such as online banking and payment processing. It also enables financial institutions to store and manage large amounts of data securely.
- Entertainment: Cloud computing is used to provide streaming services, such as Netflix and Spotify. It also enables cloud gaming, allowing users to play games without the need for high-end hardware.
The impact and implications of cloud computing on society and the environment are significant. On the one hand, cloud computing has the potential to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions by enabling more efficient use of computing resources. On the other hand, it raises concerns about data privacy and security, as well as the environmental impact of data centers. As cloud computing continues to evolve, it is important to consider these implications and work towards sustainable and responsible cloud computing practices.
How is blockchain technology being used in cloud computing?
Blockchain technology is being integrated with cloud computing to create new applications and services. The use of blockchain in cloud computing can help enterprises manage data better and ensure its security. For instance, a blockchain based system could be used to store the data collected by IoT devices in a secure and tamper-proof manner. In a block-chain-based cloud infrastructure, each node in the network is responsible for storing a copy of the blockchain. When a new transaction is added to the blockchain, all nodes in the network are updated with the new information. This allows for a decentralized, transparent, and secure way of managing data. Blockchain technology can enhance cloud computing by increasing security, improving efficiency, and enhancing traceability. Blockchain is being used in various industries and domains, such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management. Blockchain technology can be used to create a decentralized network of nodes that shares data and processing power, providing enhanced security, improved scalability, and increased availability. The combination of blockchain and cloud computing offers several advantages, including increased data security, easy traceability, improved system interoperability, and much more.
what are some challenges of integrating blockchain technology with cloud computing?
Blockchain technology is being integrated with cloud computing to create new applications and services that offer enhanced security, scalability, and decentralization. However, this integration also presents several challenges that must be addressed to fully realize the potential of block-chain in cloud computing.
Challenges of Integrating Block–chain Technology with Cloud Computing
- Technical Complexity: Integrating the block-chain with cloud computing requires a deep understanding of both technologies, which can be challenging for organizations and developers.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce: Block-chain technology is still an emerging and nascent field, so there is a shortage of skilled personnel who can execute these processes.
- Security Vulnerability: While the block-chain provides a high-security solution, the integration of the block-chain with cloud computing can introduce new security vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: Block-chain networks can be slow and less scalable compared to cloud computing, which may limit their adoption in certain applications.
- Energy Consumption: Block-chain networks, particularly those based on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, can consume a significant amount of energy.
- Compliance and Regulatory Issues: Block-chain technology may not fully comply with existing regulations, which can create challenges for organizations that want to adopt this technology.
- Integration and Transition Challenges: Block-chain-based applications may require specialized infrastructure and tools, which can be difficult to integrate with existing cloud computing platforms.
Benefits of Integrating Blockchain Technology with Cloud Computing
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology enables decentralized network management, which can improve the security and reliability of cloud computing services.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology provides a high-security solution which can help protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Cloud computing provides scalability, which can help blockchain networks overcome their inherent limitations.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud computing can help reduce the costs associated with maintaining blockchain networks.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology provides a transparent and immutable record of transactions, which can help improve the trust and accountability of cloud computing services.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing provides a flexible infrastructure that can help organizations adapt to changing business needs.
- Efficiency: Block-chain technology can help improve the efficiency of cloud computing services by reducing the need for intermediaries and streamlining processes.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology and cloud computing are complementary technologies that can help organizations overcome the challenges associated with data security, scalability, and decentralization.
However, integrating the block-chain with cloud computing also presents several challenges that must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this technology combination. By addressing these challenges, organizations can leverage the benefits of blockchain technology to create innovative and secure cloud computing solutions.