Solar energy has various environmental impacts, including effects on land use, water use, hazardous materials, greenhouse gas emissions, climate change mitigation, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. Here’s a closer look at each aspect:
Land Use, Water Use, and Hazardous Materials
The environmental impacts associated with solar power include land use and habitat loss, water use, and the use of hazardous materials. The construction of solar facilities on vast areas of land can result in soil compaction, alteration of drainage channels, and increased erosion. Additionally, some solar power plants may require water for cleaning solar collectors, which can strain available water resources in arid settings. Furthermore, solar energy technologies require materials that are energy intensive to make, and some solar thermal systems use potentially hazardous fluids, which, if leaked, could be harmful to the environment1410.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Mitigation
Solar energy plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. It is a renewable source of power that produces no harmful greenhouse gas emissions during operation. By replacing traditional sources of electricity, solar energy helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions and combat global warming. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that solar PV will become the largest source of electricity generation by 2050, accounting for 16% of global electricity generation2714.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Solar energy can impact biodiversity and ecosystem services. The construction of solar facilities on large areas of land can lead to habitat loss and affect native plant and animal species.
However, there are opportunities for solar farms to improve biodiversity by implementing strategies such as increasing native vegetation and promoting ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, pollination, and ground and stormwater management.
For instance, solar farms can be designed to enhance biodiversity and provide ecological benefits, contributing to both climate and ecological objectives.
While solar energy offers significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change, it is important to carefully consider its impact on land use, water use, hazardous materials, biodiversity, and ecosystem services.
By addressing these aspects through responsible development and technological advancements, solar energy can continue to play a vital role in a sustainable energy future.
Introduction.
What is solar energy and how does it work?
Solar energy is a renewable and sustainable energy source that harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity and heat. It works through the use of solar panels, which can be installed on residential rooftops or in large solar farms.
Solar power is considered a clean energy source as it produces no harmful greenhouse gas emissions. In this article, we will explore the environmental impact of solar energy, focusing on aspects such as land use, water use, emissions, and waste.
What are the benefits and challenges of solar energy?
Benefits and Challenges of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers numerous benefits, including being a renewable and infinite energy source, reducing electricity bills, and contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and air pollution.
However, it also presents challenges such as being weather-dependent, requiring a significant amount of space, and in some cases, being associated with the use of rare materials and pollution.
What are the objectives and scope of this article?
Objectives and Scope
The objective of this paper is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of solar energy.
This includes an in-depth analysis of its effects on land use, water use, emissions, and waste. By evaluating these aspects, we aim to shed light on the overall sustainability of solar energy and the importance of responsible development and technological advancements in mitigating its environmental impact.
what are the different types of solar panels and how do they work?
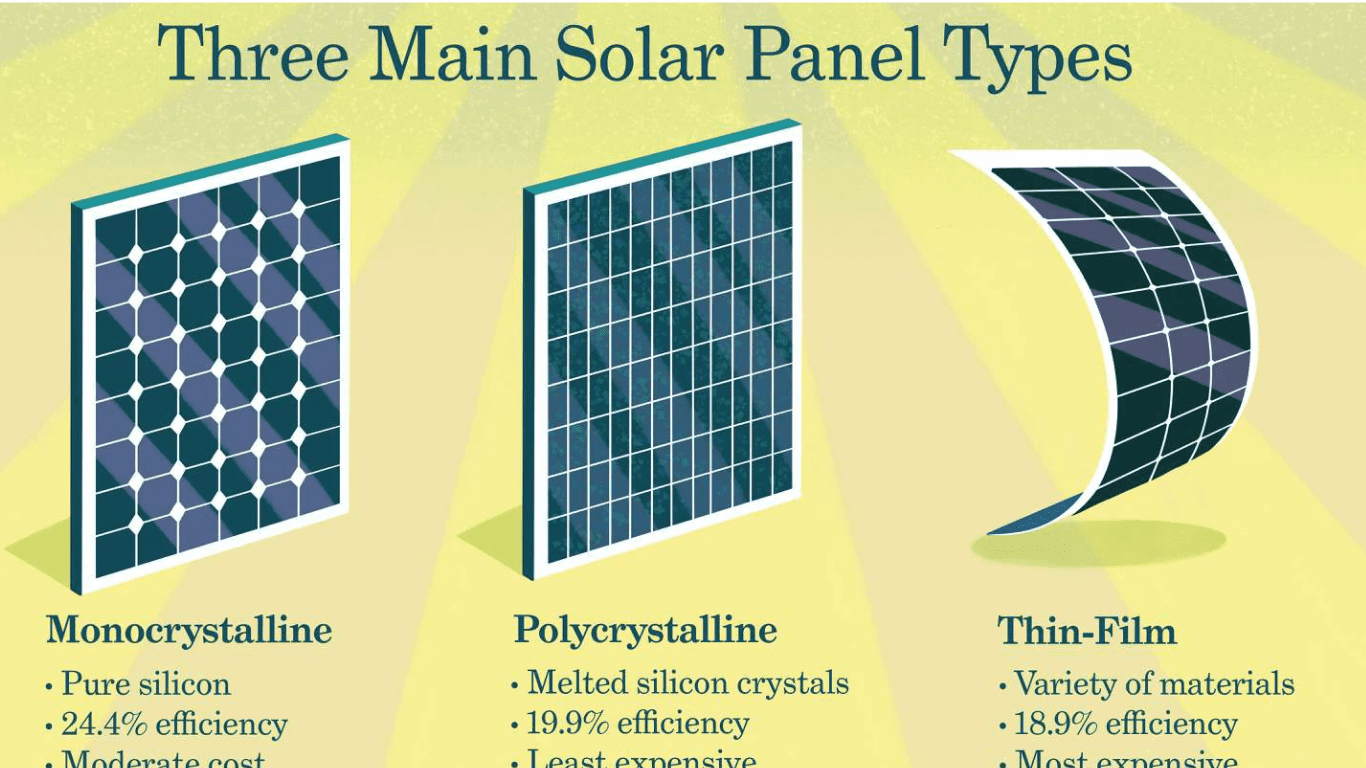
There are several types of solar panels, each with its own unique characteristics. The main types include monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels. Here’s a brief overview of each type:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels (Mono-SI)
- Efficiency Rate: Approximately 20%
- Advantages: High efficiency rate, optimized for commercial use, high lifetime value
- Disadvantages: Expensive
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels (p-Si)
- Efficiency Rate: Approximately 15%
- Advantages: Lower price
- Disadvantages: Sensitive to high temperatures, lower lifespan, slightly less space efficiency
- Thin-Film Solar Panels
- Efficiency Rate: Around 7-10%
- Advantages: Lightweight, flexible, and can be used in various applications
- Disadvantages: Require more space, less efficient than crystalline silicon panels
- Other Types
- There are also other types such as transparent, Concentrator Photovoltaics (CPV), and solar roofing shingles, each with its own specific characteristics and applications.
Now, let’s discuss how solar panels work. Solar panels work by converting energy from the sun into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photovoltaic cells, typically made of silicon, generate a flow of electricity by allowing photons to knock electrons free from atoms.
This creates a direct current (DC), which is then converted into an alternating current (AC) by an inverter for use in homes and businesses.
The benefits of solar energy include being a renewable and infinite energy source, reducing electricity bills, and contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and air pollution.
However, there are also challenges such as being weather-dependent, requiring a significant amount of space, and in some cases, being associated with the use of rare materials and pollution.
The objectives of this paper
This provide a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of solar energy, including an in-depth analysis of its effects on land use, water use, emissions, and waste.
By evaluating these aspects, the aim is to shed light on the overall sustainability of solar energy and the importance of responsible development and technological advancements in mitigating its environmental impact.
Solar Energy Production and Consumption.

How is solar energy produced and consumed in different regions and sectors?
Solar energy is produced and consumed in different regions and sectors worldwide. According to Our World in Data, solar energy consumption is measured in terawatt-hours, in terms of direct primary energy.
The data shows that solar energy generation is increasing globally, with solar photovoltaic production increasing 23% from 2019 to 2020, and it’s now the third-largest renewable electricity source worldwide, accounting for 4.5% of total global electricity generation.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that solar PV will become the largest source of electricity generation by 2050, accounting for 16% of global electricity generation.
What are the current and projected trends and scenarios of solar energy production and consumption?
The current and projected trends and scenarios of solar energy production and consumption show that renewables are set to contribute 80% of new power generation capacity to 2030 under current policy settings, with solar alone accounting for a significant portion of this growth.
The global demand for solar photovoltaic (PV) is expected to reach 1,000 GW by 2023. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that solar PV will become the largest source of electricity generation by 2050, accounting for 16% of global electricity generation.
What are the best practices and standards for measuring and reporting solar energy production and consumption?
The best practices and standards for measuring and reporting solar energy production and consumption involve using standardized units of measurement, such as terawatt-hours, and following established protocols for data collection and reporting.
The IEA provides guidelines for measuring and reporting solar energy production and consumption, including the use of standardized metrics and data collection methods.
Additionally, organizations such as the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) provide guidance on best practices for solar energy data collection and reporting.
Solar Energy Environmental Impact Assessment.

How does solar energy affect the environment in terms of land use, water use, and hazardous materials?
Solar energy has various environmental impacts, including effects on land use, water use, hazardous materials, greenhouse gas emissions, climate change mitigation, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. Here’s a closer look at each aspect:
Land Use, Water Use, and Hazardous Materials
The environmental impacts associated with solar power include land use and habitat loss, water use, and the use of hazardous materials. The construction of solar facilities on vast areas of land can result in soil compaction, alteration of drainage channels, and increased erosion.
Additionally, some solar power plants may require water for cleaning solar collectors, which can strain available water resources in arid settings.
Furthermore, solar energy technologies require materials that are energy intensive to make, and some solar thermal systems use potentially hazardous fluids, which, if leaked, could be harmful to the environment.
How does solar energy affect the environment in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and climate change mitigation?
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change Mitigation
Solar energy plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change. It is a renewable source of power that produces no harmful greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
By replacing traditional sources of electricity, solar energy helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions and combat global warming.
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that solar PV will become the largest source of electricity generation by 2050, accounting for 16% of global electricity generation.
How does solar energy affect the environment in terms of biodiversity and ecosystem services?
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Solar energy can impact biodiversity and ecosystem services. The construction of solar facilities on large areas of land can lead to habitat loss and affect native plant and animal species.
However, there are opportunities for solar farms to improve biodiversity by implementing strategies such as increasing native vegetation and promoting ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, pollination, and ground and stormwater management.
For instance, solar farms can be designed to enhance biodiversity and provide ecological benefits, contributing to both climate and ecological objectives.
In conclusion, while solar energy offers significant environmental benefits by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change, it is important to carefully consider its impact on land use, water use, hazardous materials, biodiversity, and ecosystem services.
By addressing these aspects through responsible development and technological advancements, solar energy can continue to play a vital role in a sustainable energy future.
Solar Energy Environmental Impact Management.

How can solar energy environmental impact be minimized and mitigated through design, technology, and policy?
Minimizing and Mitigating Solar Energy’s Environmental Impact:
- Design: Incorporate sustainable principles into solar panel installations to minimize ecological footprint and protect habitats.
- Technology: Invest in collaborative research to improve solar panel efficiency, durability, and affordability.
- Policy: Adhere to environmental regulations and integrate solar energy into educational institutions to promote environmental consciousness.
How can solar energy environmental impact be monitored and evaluated through indicators, tools, and methods?
Monitoring and Evaluating Solar Energy’s Environmental Impact:
- Indicators: Use standardized methods and guidelines, such as Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), to measure and analyze the impact of solar power projects on land use, biodiversity, water resources, emissions, and local communities.
- Tools: Utilize software tools and simulations to optimize system configuration, estimate energy production and costs, and conduct solar resource assessments.
- Methods: Conduct environmental and social impact assessments to identify potential effects and develop mitigation measures.
How can solar energy environmental impact be communicated and disseminated through awareness, education, and participation?
Communicating and Disseminating Solar Energy’s Environmental Impact:
- Awareness: Share experiences, promote benefits, and address myths to increase renewable energy education and awareness.
- Education: Start with the basics, encourage participation, and provide resources for further learning to spread knowledge about renewable energy.
- Participation: Engage in social media, forums, events, and classrooms to communicate the environmental benefits of solar energy.
Conclusion and Recommendations
What are the main findings and conclusions of this paper?
The main findings and conclusions of the paper “The Environmental Impact of Solar Energy: A Closer Look” are as follows:
- Solar energy has both positive and negative environmental impacts, including effects on land use, water use, emissions, waste, and biodiversity.
- The benefits of solar energy include being a renewable and infinite energy source, reducing electricity bills, and contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and air pollution.
- The challenges of solar energy include being weather-dependent, requiring a significant amount of space, and in some cases, being associated with the use of rare materials and pollution.
What are the implications and recommendations for solar energy stakeholders and decision-makers?
The implications and recommendations for solar energy stakeholders and decision-makers are:
- Stakeholders and decision-makers should consider the environmental impact of solar energy when planning and implementing solar projects.
- They should prioritize the use of sustainable design principles, invest in collaborative research to improve solar panel efficiency, and adhere to environmental regulations and policies.
What are the limitations and gaps of this paper and how can they be addressed?
The limitations and gaps of the paper include:
- The paper may not cover all the potential environmental impacts of solar energy, and there may be additional factors to consider.
- The research may be biased towards certain types of impacts, such as effects on the biophysical environment, and may not address health, economic, and social impacts in a notable manner.
These limitations can be addressed by conducting further research to comprehensively assess the environmental impact of solar energy and by ensuring a balanced focus on all relevant impact categories.
4 thoughts on “The Environmental Impact of Solar Energy: A Closer Look”