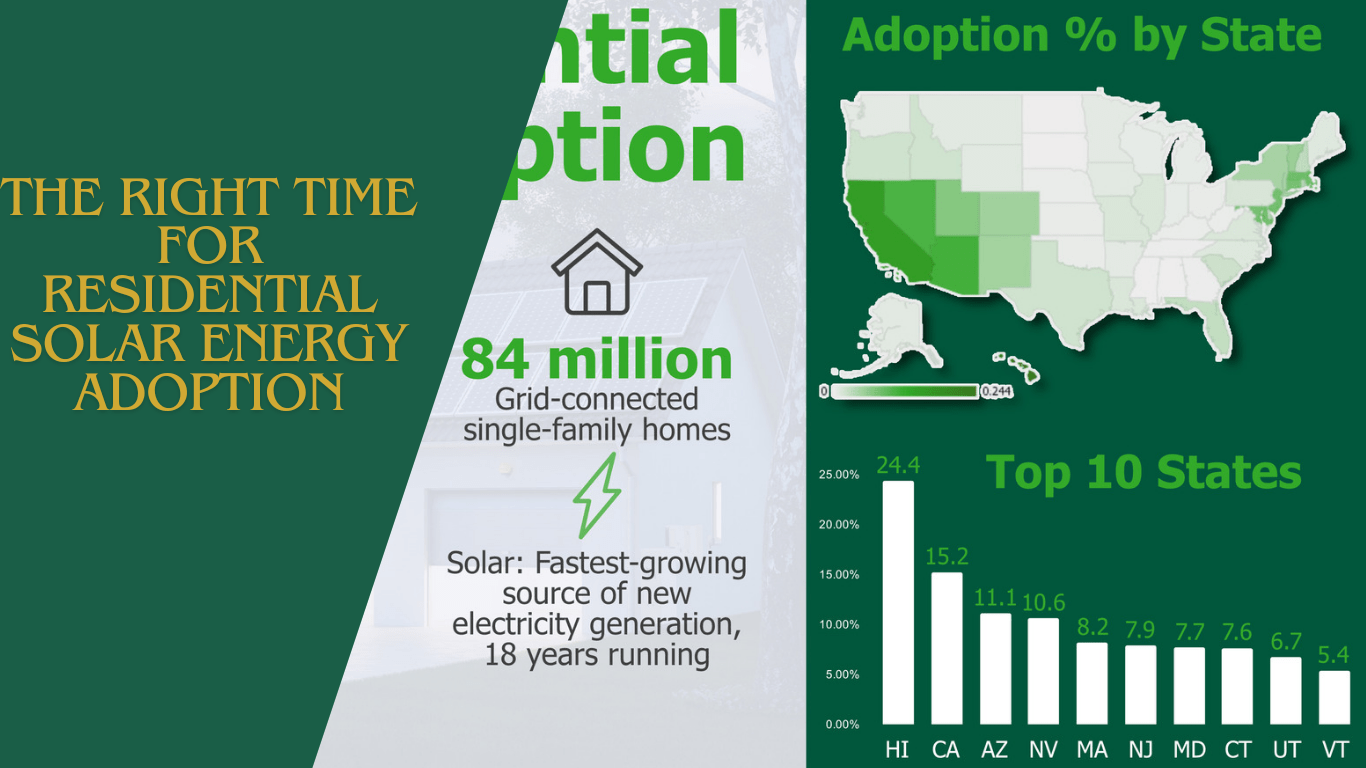
The right time for residential solar energy adoption is now. With advancements in solar panel technology, decreased costs, and government incentives, homeowners have a unique opportunity to embrace solar energy. The average installed cost for a residential solar electric system has dropped, making it more affordable for average consumers.
Additionally, the federal investment tax credit and other state incentives further reduce the cost of solar photovoltaic systems. Technological advancements, such as increased capacity and decreased costs of solar batteries, as well as the widespread use of bifacial panels and tracking systems, have made solar power more efficient and cost-effective.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of solar energy, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, make it a compelling choice for homeowners. Despite the numerous benefits, high upfront costs remain a significant barrier to adoption.
However, with the increasing demand for energy and fresh water, solar technology has emerged as a promising solution for sustainable development. As technology continues to improve and costs continue to decrease, solar energy is poised to become an even bigger player in the energy industry.
The combination of technological advancements, government incentives, and environmental benefits makes the present an opportune time for residential solar energy adoption.
Introduction.
What are the benefits and challenges of residential solar energy adoption?
The benefits of residential solar energy adoption include reduced utility bills, environmental benefits, and increased property value. Solar energy can provide energy independence, cost savings, and a long-term return on investment. It is a renewable energy source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and can increase the value of a property.
Challenges of residential solar energy adoption include high upfront costs, weather dependency, space requirements, and potential maintenance. Solar panels require a significant initial investment, and their efficiency is dependent on sunlight exposure. Additionally, the space required for installation and the potential need for maintenance are important considerations.
What are the main factors and criteria for determining the right time for residential solar energy adoption?
The main factors and criteria for determining the right time for residential solar energy adoption include the trend of rising energy costs, energy consumption patterns, available sunlight, and financial viability.
The combination of technological advancements, government incentives, and environmental benefits also plays a crucial role in determining the opportune time for residential solar energy adoption.
What are the objectives and scope of this article?
The objectives of this article are to highlight the benefits of solar energy adoption, discuss the challenges associated with it, and provide an overview of the factors and criteria for determining the right time for residential solar energy adoption.
The scope of the article is to inform homeowners about the advantages and obstacles of adopting residential solar energy and to emphasize the current opportune time for its adoption based on various factors and advancements in the solar energy industry.
Residential Solar Energy Market and Trends.

How is the residential solar energy market growing and evolving in different regions and countries?
The residential solar energy market is growing and evolving in different regions and countries, with significant developments and projections. According to a report, the residential solar energy market size is projected to reach multimillion USD by 2029, with North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East and Africa being the leading regions in this market.
The market is expected to grow considerably in North America, especially in the United States, during the forecast period, due to high adoption of advanced technology and the presence of large players in the industry. Additionally, the Asia-Pacific region is estimated to grow at the highest CAGR over the forecast period, with China, India, Japan, and Australia being key contributors to this growth5.
What are the drivers and barriers of residential solar energy adoption in different contexts and scenarios?
The drivers of residential solar energy adoption include technological innovation, decreasing hardware costs, and government incentives. These factors have driven down the installed price of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and spurred adoption.
On the other hand, the barriers to residential solar energy adoption encompass high upfront costs, weather dependency, and space requirements. High installation prices and upfront costs are major barriers to residential solar panel adoption, despite the interest in saving on utility bills.
What are the best practices and examples of successful and innovative residential solar energy projects and programs?
Best practices and examples of successful and innovative residential solar energy projects and programs involve essential steps for successful solar project management, from planning and design to execution and maintenance. These practices include developing a clear project plan, continuously evaluating the system’s performance, and communicating effectively with all stakeholders.
Furthermore, the use of high-quality solar panels, inverters, and other equipment, as well as the establishment of clear rules and pathways for developers applying for a construction permit, are considered best practices in the industry. In conclusion, the residential solar energy market is experiencing significant growth and evolution, with various regions and countries contributing to this expansion.
While drivers such as technological innovation and government incentives are propelling adoption, barriers like high upfront costs and weather dependency continue to challenge the widespread implementation of residential solar energy. By following best practices and examples of successful projects, the industry can overcome these barriers and further promote the adoption of residential solar energy.
Residential Solar Energy Technologies and Solutions.

What are the different types and characteristics of residential solar energy technologies and solutions?
Residential solar energy technologies and solutions encompass various types, each with its own characteristics, applications, and benefits. The main types of residential solar energy systems include on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems. On-grid systems are connected to the utility grid and are suitable for areas with a reliable grid connection. Off-grid systems are independent and suitable for rural areas or locations with a weak or no grid connection.
Hybrid systems combine the features of both on-grid and off-grid systems, offering flexibility and energy independence. Solar panels, also known as solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, are a common residential solar energy technology. They convert sunlight into electricity and can cover a significant portion of a household’s electricity demand.
However, they are dependent on sunlight and may have high upfront costs. Despite this, they offer benefits such as reduced electricity bills, environmental friendliness, and potential earnings from excess energy production.
Advancements in solar panel technologies, such as longer-lasting solar cells and the development of innovative applications like solar paints and transparent solar windows, are revolutionizing the renewable energy industry.
What are the current and potential applications and benefits of residential solar energy technologies and solutions in various settings and situations?
Additionally, the characteristics of solar panels, such as their durability, low maintenance, and ability to provide constant and consistent power, make them an attractive option for residential use. The benefits of residential solar energy technologies and solutions include reduced utility bills, energy independence, environmental friendliness, and potential earnings from excess energy production. However, challenges such as high upfront costs, weather dependency, and space requirements should be considered.
The current and potential applications of residential solar energy technologies are diverse, ranging from powering individual homes to contributing to grid resilience and job creation. By understanding the different types, characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of residential solar energy technologies, homeowners can make informed decisions about adopting solar energy for their residences.
What are the differences between on-grid and off-grid solar pv systems for residential use?
The differences between on-grid and off-grid solar PV systems for residential use are significant and impact their suitability for different situations. On-grid systems are connected to the electric grid and supplement the power received from the utility. They do not require battery storage and are suitable for areas with a reliable grid connection.
On the other hand, off-grid systems are entirely independent and rely on battery storage. They are not connected to the electric grid and are suitable for remote locations or areas were connecting to the grid is not practical or feasible. Despite their differences, both systems offer similar benefits, such as reducing energy costs and providing clean, renewable energy.
The advantages of on-grid systems include the ability to participate in net metering, lower initial costs, and the availability of grid power as a backup. However, they are dependent on the grid and do not provide energy independence. Off-grid systems offer complete energy independence and are not affected by power outages. They are suitable for remote or rural areas where grid power is not available.
However, they require additional equipment like batteries, which can lead to higher initial expenses. In summary, the choice between on-grid and off-grid solar PV systems depends on various factors, including the reliability of the grid, the location, energy requirements, and the level of energy independence desired.
On-grid systems are suitable for areas with a reliable grid connection and can offer cost savings through net metering, while off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations and provide complete energy independence, albeit at a higher initial cost.
Residential Solar Energy Policies and Incentives.
Solar energy policies and incentives vary by country. Here are some examples of policies and incentives for residential solar energy in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia:
United States
The federal government offers a tax credit for residential solar photovoltaics, or PV. The investment tax credit (ITC) offers a direct reduction in taxes owed as an incentive for installing a new solar energy system1. The credit is limited to 30% of qualified expenditures made for property placed in service in a given year. Additionally, some states and local governments offer their own incentives for solar energy.
United Kingdom
The UK government offers the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG), which allows homeowners to earn money by generating extra electricity from their solar panels. The government also offers the Canada Greener Homes Grant, which provides a grant of up to £5,600 for qualifying energy-efficient retrofits and up to £600 for EnerGuide evaluations. Additionally, local councils across the UK offer various grants and incentives to encourage solar panel installations.
Canada
The Canada Greener Homes Grant provides a grant of up to $5,600 for qualifying energy-efficient retrofits and up to $600 for EnerGuide evaluations. Homeowners can also receive the Canada Greener Homes Loan, a 10-year interest-free loan from $5,000 to $40,000. Additionally, some provinces and cities offer their own incentives and rebates to further encourage the adoption of solar technology.
Australia
The Australian government offers the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme, which provides a benefit towards the purchase cost of small-scale renewable energy systems, such as solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, hydro systems, solar water heaters, and air source heat pumps. Installing an eligible system allows the creation of small-scale technology certificates (STCs) with a value that can be redeemed by selling or assigning them4.It’s important to note that policies and incentives can change over time, so it’s a good idea to check with local authorities and organizations for the most up-to-date information.
What are the solar incentives available in canada?
Canada offers several incentives for residential solar energy. The federal government provides the Canada Greener Homes Grant, which offers a solar rebate of $1,000/kW up to a maximum of $5,0001. Homeowners can also receive the Canada Greener Homes Loan, a 10-year interest-free loan from $5,000 to $40,000.
Additionally, some provinces and cities offer their own incentives and rebates to further encourage the adoption of solar technology. For example, Efficiency Manitoba offers a rebate of up to $0.50 per watt, up to a maximum of 10 kilowatts or $5,000 per home for residential solar systems.
The Government of Yukon is currently offering a rebate of $0.80 per watt up to $5,000 through the Good Energy Renewable Energy Rebate. It’s important to note that policies and incentives can change over time, so it’s a good idea to check with local authorities and organizations for the most up-to-date information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the right time for residential solar energy adoption depends on various factors, including the initial investment, financial incentives, energy savings, net metering, and environmental benefits. Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, with a slight decrease in efficiency after 30 years.
The initial investment in solar panels can be significant, but the cost has been decreasing over the years due to technological advancements and increased market competition.
Governments and local authorities offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage the adoption of solar energy. In Canada, the federal government provides the Canada Greener Homes Grant, which offers a solar rebate of $1,000/kW up to a maximum of $5,000.
Homeowners can also receive the Canada Greener Homes Loan, a 10-year interest-free loan from $5,000 to $40,000. Additionally, some provinces and cities offer their own incentives and rebates to further encourage the adoption of solar technology.
It is advisable to stay informed about the latest policies and incentives by checking with local authorities and organizations due to potential changes over time. Ultimately, the decision to adopt residential solar energy should be based on a careful consideration of the costs and benefits, as well as the individual circumstances of the homeowner
1 thought on “The Right Time for Residential Solar Energy Adoption”