
The article will focus on economic impact, environmental benefits, and challenges and solutions related to the adoption of solar energy in developing countries. It will highlight the potential of solar energy to drive economic growth, create job opportunities, and improve access to electricity, while also addressing environmental concerns and offering sustainable solutions.
The article will discuss the role of governments, international organizations, and stakeholders in promoting the adoption of solar energy and the need to overcome challenges such as initial investment costs, technological knowledge gaps, and supportive policies.
It will also emphasize the importance of collaborative efforts to unlock the full potential of solar energy and bring about positive and lasting change in the lives of millions across the globe.
The article will include important keywords such as “solar energy,” “developing nations,” “economic impact,” “environmental benefits,” “job opportunities,” “energy access,” “sustainable development,” “challenges,” and “solutions.
The Potential of Solar energy in Developing Nation.
“The potential of solar energy in developing nations is significant, with the ability to drive economic growth, create job opportunities, improve access to electricity, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
The falling cost of solar energy has made it an increasingly viable option for developing countries, offering reliable and cost-effective energy solutions.
However, challenges such as initial investment costs, technological knowledge gaps, and the need for supportive policies must be addressed to fully realize the potential of solar energy in these regions.
By overcoming these challenges and promoting the adoption of solar energy, governments, international organizations, and stakeholders can contribute to sustainable development and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.
What is solar energy and why is it important for developing nations?
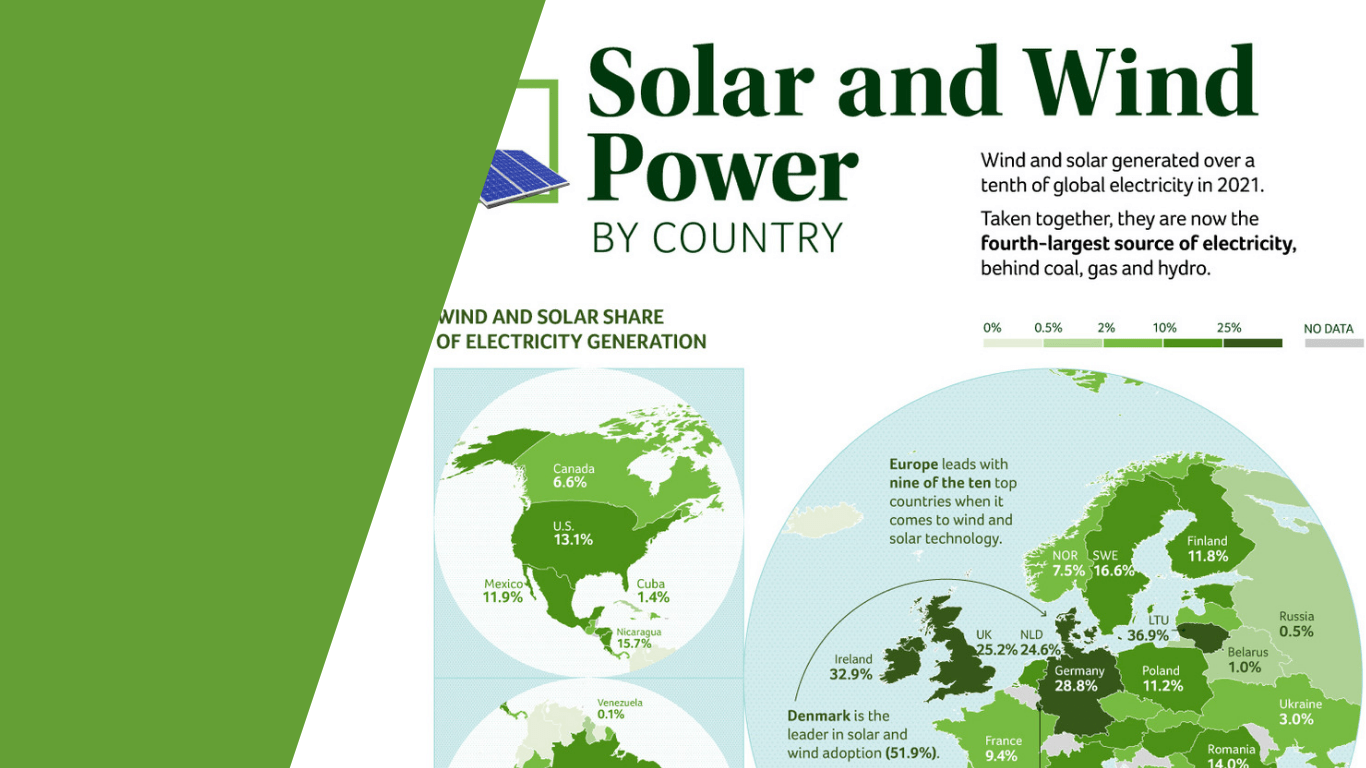
a. Solar Energy and its Importance for Developing Nations
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that can be harnessed using various technologies, such as solar power, to generate electricity or provide heat.
It is an essential source of renewable energy, with the potential to satisfy all future energy needs if suitably harnessed. In developing nations, solar energy is of great importance for several reasons.
- Economic Impact: Solar energy can drive economic growth and create job opportunities. Recent advances in technology have led to a significant decrease in the cost of solar power, making it more accessible and affordable than ever before.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar power is a clean and renewable energy source that creates no harmful greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar energy mitigates greenhouse gas emissions and minimizes the environmental impact associated with traditional energy sources.
- Energy Access: Many developing countries face energy poverty, with a significant portion of the population lacking access to electricity. Solar energy provides a sustainable, affordable, and reliable source of electricity, thereby improving energy access in these regions.
- Sustainable Development: Solar energy plays a pivotal role in promoting energy access, preserving the environment, and encouraging technological innovation, making it a significant resource for countries aiming for sustainable development.
b. Challenges and Opportunities of Solar Energy in Developing Nations
The main challenges and opportunities of solar energy in developing nations are as follows:
- Challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: The initial cost of setting up solar energy infrastructure can be a barrier for many developing countries.
- Technological Knowledge Gaps: Limited technical expertise and knowledge about solar energy systems can hinder their effective implementation.
- Supportive Policies: The absence of supportive policies and regulatory frameworks can impede the widespread adoption of solar energy.
- Opportunities:
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: Solar energy initiatives stimulate economic growth and create job opportunities in developing countries.
- Environmental Conservation: Solar energy promotes environmental sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Access: Solar power provides a sustainable and reliable source of electricity, improving energy access in remote and underserved areas.
c. Aims and Scope of the Article?
This article aims to shed light on the economic impact, environmental benefits, and challenges and solutions related to the adoption of solar energy in developing countries.
It will highlight the potential of solar energy to drive economic growth, create job opportunities, and improve access to electricity, while also addressing environmental concerns and offering sustainable solutions.
The article will discuss the role of governments, international organizations, and stakeholders in promoting the adoption of solar energy and the need to overcome challenges such as initial investment costs, technological knowledge gaps, and supportive policies.
It will emphasize the importance of collaborative efforts to unlock the full potential of solar energy and bring about positive and lasting change in the lives of millions across the globe.
Solar Energy Technologies and Applications
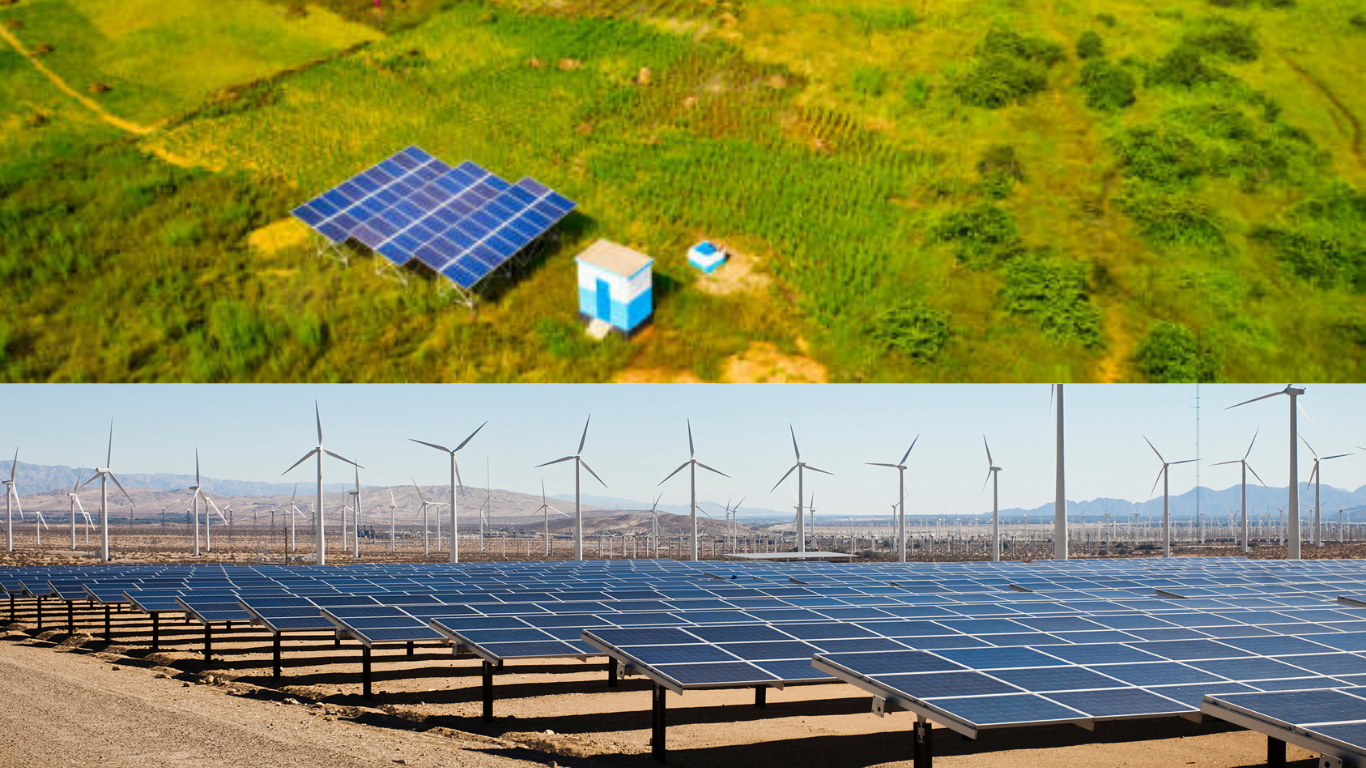

What are the different types and characteristics of solar energy technologies?
a. Types and Characteristics of Solar Energy Technologies
Solar energy technologies encompass various methods of harnessing solar power, each with its own characteristics and applications. The main types of solar energy technologies include:
- Passive Solar Gain: This involves designing buildings to utilize the sun’s heat without the use of mechanical systems.
- Solar Thermal: This technology is used for heating and can be applied in both low-temperature solar thermal (e.g., heating water) and high-temperature solar thermal (e.g., generating electricity).
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small area, which then produces heat to drive a steam turbine and generate electricity.
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV): PV technology directly converts sunlight into electricity using panels made of semiconductor cells.
b. Current and Potential Applications of Solar Energy in Developing Nations.
The current and potential applications of solar energy in developing nations are diverse and include:
- Electricity Generation: Solar energy can be used to generate electricity, providing a reliable and sustainable power source for homes, businesses, and communities.
- Water Desalination: Solar energy can be utilized to desalinate water, addressing water scarcity issues in many developing regions.
- Agricultural Use: Solar energy can power irrigation systems, improving agricultural productivity in rural areas.
- Healthcare Facilities: Solar energy can provide a consistent power source for essential medical equipment in remote healthcare facilities.
- Rural Electrification: Solar energy can be used to bring electricity to off-grid and remote areas, improving the quality of life for those communities.
c. Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Energy Technologies and Applications.
i. Advantages
The advantages of solar energy technologies and applications include:
- Renewable Energy Source: Solar energy is abundant and renewable, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Reduction in Electricity Bills: Solar energy can lead to significant cost savings on electricity bills for individuals and communities.
- Diverse Applications: Solar energy can be used for various purposes, including electricity generation, water desalination, and agricultural use.
- Low Maintenance Costs: Solar energy systems generally have low maintenance requirements.
ii. Disadvantages
The disadvantages of solar energy technologies and applications include:
- High Initial Costs: The initial investment for setting up solar energy infrastructure can be a barrier, particularly for developing countries.
- Weather Dependency: Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, making it less reliable during periods of low sunlight or at night.
- Space Requirements: Solar energy systems may require significant space for installation, which can be a limitation in some areas.
- Energy Storage Costs: The cost of storing solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight can be expensive.
Solar Energy Policies and Strategies
a. What are the existing and emerging policies and strategies for promoting solar energy in developing nations?
Existing and Emerging Policies and Strategies for Promoting Solar Energy in Developing Nations.
The existing and emerging policies and strategies for promoting solar energy in developing nations are essential for achieving decarbonization, economic growth, and energy security. However, the effectiveness of these policies has been a subject of concern. Research indicates the need to strengthen the institutional capacity of emerging economies, especially low-income countries, to secure finance for decarbonization projects. This highlights the importance of fulfilling commitments made during the Paris Agreement and the need for a combination of policies extending beyond regulatory measures, such as phasing out fossil fuel subsidies to strengthen market signals for decarbonization.
What are the drivers and barriers of solar energy policies and strategies in developing nations?
Drivers and Barriers of Solar Energy Policies and Strategies in Developing Nations.
The drivers of solar energy policies and strategies in developing nations include the potential for economic growth, energy security, and environmental sustainability. However, several barriers exist, such as high initial investment costs, technological knowledge gaps, and the absence of supportive policies and regulatory frameworks. These barriers hinder the effective implementation of solar energy systems and the achievement of decarbonization outcomes.
What are the best practices and lessons learned from solar energy policies and strategies in developing nations?
Best Practices and Lessons Learned from Solar Energy Policies and Strategies in Developing Nations.
Good practices and lessons learned from solar energy interventions in developing nations include the importance of properly assessing needs and requirements to ensure energy-efficient systems, the provision of awareness programs on system maintenance, and the creation of job opportunities and community engagement through the increasing use of solar systems. Additionally, the need for simplified and accelerated access to financing, the elimination of energy poverty, and the investment in renewable energy infrastructure have been emphasized as crucial for achieving a just energy transition and enhancing resilience and access to sustainable energy.
In conclusion, while there are significant opportunities for promoting solar energy in developing nations, it is essential to address the existing barriers and learn from the best practices to achieve effective and sustainable implementation. This can be done through the development of comprehensive policies, the provision of financial support, and the promotion of community engagement and awareness programs.
a. What are the expected and observed impacts and outcomes of solar energy in developing nations?
The expected and observed impacts and outcomes of solar energy in developing nations are significant. Solar energy contributes to economic, social, and environmental development, as well as addressing energy access, security, and equity issues.
Expected and Observed Impacts and Outcomes:
- Solar energy technologies will address regional and local environmental matters, reduce poverty, greenhouse gas emissions, and increment energy security.
- Solar panels have the power to uplift communities, bridging the energy gap and propelling individuals towards a better and more sustainable future. By embracing solar power, developing countries can enhance their energy security and achieve greater self-sufficiency.
- Solar energy plays a pivotal role in the development of countries by driving economic growth, promoting energy access, and preserving the environment. Its ability to boost energy independence, encourage technological innovation, and create employment makes it a significant resource for countries aiming for sustainable development.
b. How does solar energy contribute to the economic, social, and environmental development of developing nations?
Contribution to Economic, Social, and Environmental Development:
- Solar energy stimulates economic growth, improves living conditions, and protects the environment. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, leading to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality5.
- Solar power empowers developing nations by providing accessible and affordable electricity, leading to economic growth, improved living conditions, and reduced climate impact8.
- The growth of the solar energy industry creates new job opportunities, stimulates local economies, and reduces dependence on fossil fuels, leading to economic growth and improved quality of life10.
c. How does solar energy address the energy access, security, and equity issues in developing nations?
Addressing Energy Access, Security, and Equity Issues:
- Solar energy reduces energy poverty, enhances energy security, and provides sustainable, affordable, and reliable access to electricity, thereby improving the quality of life for millions in developing nations9.
- The integration of solar energy helps combat climate change, reduces air pollution, and leads to improved public health and environmental preservation. It also stimulates economic growth and creates employment opportunities13.
- Solar energy provides a decentralized approach to power generation, making it easily accessible even in remote areas, thus addressing energy access and equity issues4.
Solar energy has a transformative impact on developing nations, contributing to economic growth, social development, and environmental sustainability, while also addressing energy access, security, and equity issues. By embracing solar power, these countries can pave the way towards a prosperous and sustainable future.
Conclusion
What are the main findings and conclusions of this article?
The main findings and conclusions of the article “The Potential of Solar Energy in Developing Nations” are as follows:
- Solar energy has the potential to drive economic growth, create job opportunities, improve access to electricity, and contribute to environmental sustainability in developing nations.
- The falling cost of solar energy has made it an increasingly viable option for developing countries, offering reliable and cost-effective energy solutions.
- Challenges such as initial investment costs, technological knowledge gaps, and the need for supportive policies must be addressed to fully realize the potential of solar energy in these regions.
- Governments, international organizations, and stakeholders play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of solar energy and overcoming these challenges to contribute to sustainable development and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change.
What are the recommendations and suggestions for improving the potential and performance of solar energy in developing nations?
The recommendations and suggestions for improving the potential and performance of solar energy in developing nations include:
- Strengthening institutional capacity in emerging economies, especially low-income countries, to secure finance for decarbonization projects.
- Creating an enabling environment and strengthening policies to leverage renewable energy sources, with a focus on improving data quality and reliability to track and measure progress.
- Simplifying and accelerating access to financing for developing countries to achieve universal access to electric service and accelerate the just energy transition.
- Investing in renewable energy infrastructure, eliminating energy poverty, and fostering a just energy transition to ensure sustainable and equitable access to energy.
What are the limitations and gaps of this article and how can they be addressed?
The limitations and gaps of the article include:
- The need for more comprehensive research on the behavioral aspects of residential solar energy utilization, particularly in specific regions such as Texas, to maximize its value and outperform conventional counterparts.
- The lack of systematic research focusing on the behavioral aspects of residential solar energy utilization and the need for further improvement in the energy efficiency of solar energy utilization.
- The absence of research in solar energy regarding the Sustainable Development Goals, particularly in the areas of poverty reduction, education, gender equality, industry, innovation, infrastructure, reduced inequality, and peace and justice.
In conclusion, while the article provides valuable insights into the potential of solar energy in developing nations, there is a need for more comprehensive research and a focus on addressing the behavioral aspects of solar energy utilization and its alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals.