India has set an ambitious target to achieve about 50 GW of solar power by 2024. Solar energy technologies in India.
SOLAR ENERGY: Way Forward for Solar Energy Players in IndiaThe government has launched various schemes to encourage the generation of solar power in the country, including VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme, and more.
The solar energy sector in India has emerged as a significant player in the renewable energy market, with enormous potential for growth. The solar market in India is estimated to be at 79.07 GW by the end of this year and is projected to reach 195.11 GW after five years, registering a CAGR of 19.8%.
The main focus of the article is to discuss the challenges, opportunities, and the way forward for solar energy players in India. The article will cover topics such as government policies, market trends, and challenges faced by the solar industry in India.
Introduction.
What is the current status and future potential of solar energy in India?
India’s solar energy potential is vast, with abundant sunlight resources and a solar energy potential of about 5,000 trillion kWh per year. The country is poised to lead in sustainable energy, and the future of solar power in India appears bright, with significant growth expected in the coming years. The solar industry is expected to witness increased capacity addition, growth of rooftop solar, emphasis on energy storage, adoption of floating solar, and increased investment in solar projects, making it a crucial player in achieving India’s energy goals.The future potential of solar energy in India is immense, with the country’s commitment to expanding solar power generation and creating a greener future.
What are the main challenges and opportunities for solar energy players in India?
The Indian solar industry is expected to witness significant growth, increased capacity addition, and a focus on innovative solar technologies such as floating solar. With the government’s ambitious targets and favorable policy environment, the solar industry is set to play a crucial role in India’s sustainable energy future.
What are the objectives and scope of this article?
The objectives and scope of the article are to provide insights into the challenges, opportunities, and future potential of the solar energy sector in India. The article will cover the following key areas:
- Introduction: The article will begin with an overview of India’s ambitious solar energy targets and the government’s initiatives to promote solar power generation in the country.
- Government Policies and Schemes: It will discuss the various schemes and policies launched by the Government of India to encourage the generation of solar power, such as the VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, and Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme.
- Market Trends and Potential: The article will highlight the significant growth and potential of the solar energy market in India, with the solar market estimated to reach 79.07 GW by the end of the year and projected to reach 195.11 GW after five years, registering a CAGR of 19.8%.
- Challenges and Opportunities: It will delve into the main challenges faced by solar energy players in India, such as policy uncertainty, land acquisition, and import dependency, along with the opportunities, including job creation, export potential, and the scope for renewable energy targets.
- Way Forward: The article will provide recommendations and a way forward for solar energy players in India, considering the need for continued policy support, investment in research and development, and the promotion of domestic manufacturing to reduce import dependency.
By addressing these key areas, the article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the solar energy landscape in India, along with the challenges, opportunities, and the path forward for solar energy players in the country.
Solar Energy Market and Industry in India

How is the solar energy market and industry growing and evolving in India?
India’s solar energy market has been growing rapidly, with the solar market estimated to reach 79.07 GW by the end of 2024 and projected to grow to 195.11 GW by 2028, registering a CAGR of 19.8%. The main drivers of solar energy development in India are energy reforms, the urgency of GHG emission reduction, energy security, and employment.
What are the drivers and barriers of solar energy development and deployment in India?
However, there are several barriers to the deployment of renewable energy, including economic, institutional, technical, and socio-cultural barriers.
The Indian government has launched various schemes and policies to encourage solar power generation, such as the VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, and Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme.
The main challenges faced by solar energy players in India include policy uncertainty, land acquisition, and import dependency, while the opportunities include job creation, export potential, and the scope for renewable energy targets.
What are the best practices and examples of successful and innovative solar energy projects and programs in India?
Some of the best practices and examples of successful and innovative solar energy projects and programs in India include the Charanka Solar Park, the Rajasthan Solar Park, and the rooftop solar installations. The way forward for solar energy players in India includes continued policy support, investment in research and development, and the promotion of domestic manufacturing to reduce import dependency.
what are the successful solar energy projects in india?
India has emerged as a prominent player in the global solar industry, with numerous solar farms and power plants across the country. Some of the successful solar energy projects in India include the Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Power Project in Madhya Pradesh, the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, the Kurnool Ultra Mega Solar Project in Andhra Pradesh, the Pavagada Solar Park in Karnataka, and the Kamuthi Solar Power Project in Tamil Nadu.
These solar power projects exemplify India’s commitment to harnessing renewable resources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The Indian government has launched various schemes and policies to encourage solar power generation, such as the VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, and Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme.
The solar energy sector in India is estimated to reach 79.07 GW by the end of 2024 and projected to grow to 195.11 GW by 2028, registering a CAGR of 19.8%. The main drivers of solar energy development in India are energy reforms, the urgency of GHG emission reduction, energy security, and employment.
However, there are several barriers to the deployment of renewable energy, including economic, institutional, technical, and socio-cultural barriers.
what are the major solar energy projects currently underway in india?
India has made significant strides in adopting solar energy on a large scale, and there are several major solar energy projects currently underway in the country.
Some of the notable solar energy projects include the Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Power Project in Madhya Pradesh, the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, the Kurnool Ultra Mega Solar Project in Andhra Pradesh, the Pavagada Solar Park in Karnataka, and the Kamuthi Solar Power Project in Tamil Nadu.
These projects are part of India’s ambitious target to achieve 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, which expands to 500 GW by 2030.
The Indian government has launched various schemes and policies to encourage solar power generation, such as the VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, and Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme. Despite the progress, there are still challenges to the deployment of renewable energy, including economic, institutional, technical, and socio-cultural barriers.
However, the future potential of solar energy in India is bright, with the country poised to lead in sustainable energy and transform its energy landscape.
Solar Energy Policies and Regulations in India
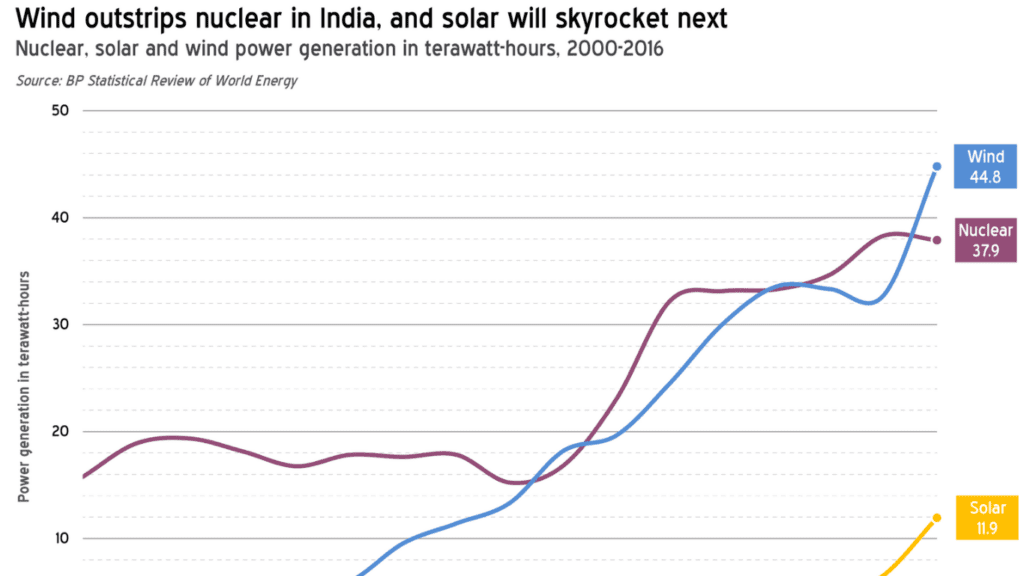
What are the existing and emerging policies and regulations for promoting and governing solar energy in India?
The solar energy sector in India is governed by various policies and regulations aimed at promoting and regulating solar energy. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) is responsible for enforcing renewable energy laws in India, including those related to solar energy.
The government has implemented several schemes and policies to encourage solar power generation, such as the VGF Schemes, CPSU Scheme, Defence Scheme, Canal bank & Canal top Scheme, Bundling Scheme, and Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Scheme.
Additionally, the Electricity Act of 2003 provides a framework for solar energy policy, including provisions for preferential tariffs and quotas for renewable energy.
What are the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders and actors in the solar energy sector in India?
The roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders in the solar energy sector in India vary. Stakeholders include the government, investors, developers, EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) companies, operation and maintenance service providers, consumers, and various industry associations.
For example, investors and developers are responsible for funding and implementing solar projects, while EPC companies are involved in the design, procurement, and construction of solar installations.
Operation and maintenance companies are responsible for the ongoing upkeep of solar plants, and consumers are key stakeholders in the adoption of solar energy.
What are the best practices and standards for developing and implementing solar energy policies and regulations in India?
Best practices and standards for developing and implementing solar energy policies and regulations in India are outlined in various guidelines and reports. For instance, the EPC Best Practice Guidelines: India Edition provides key national legislation on occupational health and safety for EPC service providers, ensuring awareness of their obligations.
The O&M Best Practice Guidelines: India Edition aims to increase quality and transparency in the operation and maintenance of solar power plants, involving owners, investors, lenders, and technical advisors.
Furthermore, the MNRE has published various resources, including best practices manuals, bidding documents, and state-specific policies and regulations, to support the development and implementation of solar energy projects.
The solar energy sector in India is governed by a range of policies and regulations, with diverse stakeholders playing crucial roles in the industry. Best practices and standards are available to guide the development and implementation of solar energy policies and projects, contributing to the growth and sustainability of the sector.
Solar Energy Technologies and Solutions in India
What are the different types and characteristics of solar energy technologies and solutions available and suitable for India?
India has a diverse range of solar energy technologies and solutions, each with its own characteristics and applications. The main types of solar energy technologies include:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy: This technology converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large utility-scale power plants1.
- Solar Thermal Energy (STE): Solar thermal energy harnesses the sun’s heat to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling for various applications. It is particularly suitable for industrial process heat, desalination, and space heating1.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small area, typically to generate steam and drive a turbine for electricity generation. This technology is well-suited for large-scale power plants1.
- Passive Solar: Passive solar design uses the sun’s energy for heating and cooling living spaces directly, without the use of mechanical or electrical devices. It is commonly used in building design to maximize natural light and heat1.
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): BIPV integrates solar modules into the building envelope, such as the roof or facade, to generate electricity while serving as a structural or design element. It is suitable for new construction and building retrofits.
What are the current and potential applications and benefits of solar energy technologies and solutions in various sectors and regions in India?
The current and potential applications of these solar energy technologies in India are diverse. Solar PV is widely used for off-grid and grid-connected applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Solar thermal technologies are suitable for industrial process heat, desalination, and space heating. The benefits of solar energy technologies in India include cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and their potential to provide reliable power, especially in rural areas. Solar energy also offers benefits such as reduced dependence on imported oil, job creation, and improved living standards in remote areas.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy technologies and solutions in India?
While solar energy technologies offer numerous advantages, such as being a clean and reliable energy source, they also have some limitations. The main advantages of solar energy technologies in India include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Solar energy is becoming increasingly cost-competitive, especially in regions with high solar irradiance, such as India.
- Environmentally Friendly: Solar energy helps reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change, making it an ideal energy source for India.
- Reliability: Solar energy provides a reliable source of power, particularly in rural areas with limited access to traditional energy sources.
- Job Creation: The solar energy sector has the potential to create employment opportunities, particularly in the renewable energy industry.
Despite these advantages, solar energy technologies also have some limitations, including:
- Intermittency: Solar energy generation is dependent on sunlight, making it intermittent and requiring energy storage or backup power sources for continuous supply.
- Land Requirement: Large-scale solar power plants require significant land area, which can be a limitation in densely populated or agriculturally intensive regions.
- Import Dependency: India currently relies on imported solar panels and components, which can be a barrier to achieving energy independence.
Solar energy technologies offer a wide range of applications and benefits in India, including cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and reliability. However, they also have limitations, such as intermittency and land requirements, that need to be addressed for their widespread adoption and integration into the energy landscape.
Solar Energy Impacts and Outcomes in India.
How does solar energy affect the economic, social, and environmental outcomes in India?
Solar energy has significant economic, social, and environmental impacts in India. The adoption of solar energy has led to the creation of employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas, where solar farms and rooftop installations are prevalent. Solar energy has also helped in improving access to electricity in remote areas of India, contributing to social inclusivity and economic development. The shift towards sustainable energy sources aligns with the “E” aspect of ESG, demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship.
How does solar energy contribute to the national and global goals of clean energy transition and climate change mitigation?
Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power, which significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources, making it an ideal energy source for India.
However, the rapid expansion of solar energy in India poses challenges in the context of cropland encroachment and water-resource scarcity. The Indian government has pledged to invest $4.3 billion in green technology to clean up the country, largely focusing on green hydrogen and solar power from the Himalayan region of Ladakh.
The growth of the Indian solar industry has had a positive impact on the economy, including the creation of job opportunities, a reduction in the country’s carbon footprint, and improved access to electricity.
What are the best practices and standards for measuring and reporting the impacts and benefits of solar energy in India?
The best practices and standards for measuring and reporting the impacts and benefits of solar energy in India include forecasting and environmental impact assessment, waste management and recycling, and the adoption of decentralized, community-owned renewable energy systems.
what are the most promising solar energy technologies for india’s energy needs?
India’s clean energy transition is rapidly underway, with a focus on solar energy technologies. The most promising solar energy technologies for India’s energy needs include:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy: Solar panels are becoming increasingly cost-competitive, especially in regions with high solar irradiance, such as India. The country is well-suited for the development and installation of utility-scale power plants, making PV solar energy a promising technology.
- Solar Thermal Energy (STE): Solar thermal technologies are suitable for industrial process heat, desalination, and space heating, offering potential applications in various sectors in India.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): CSP, which uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight, is well-suited for large-scale power plants and has the potential to contribute to India’s clean energy transition.
- Advanced Solar Technologies: India is also embracing advanced solar technologies, such as thin, flexible solar panels, solar farms on water, and solar paint, reflecting a commitment to a sustainable energy future.
These technologies are essential for India’s ambitious renewable energy targets, including the installation of 450 GW of renewable capacity by 2030, and the country’s commitment to becoming a global leader in renewable energy.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Findings
- Promising Solar Technologies: Solar PV, Solar Thermal, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP), and Advanced Solar Technologies are promising for India’s energy needs.
- Challenges and Opportunities: India faces challenges such as limited availability of natural resources, geographical limitations, financial constraints, and variability in sunlight. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation and collaboration.
- Economic and Environmental Benefits: Solar energy offers cost-effective and environmentally sustainable solutions to India’s energy needs, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Government Initiatives: The Indian government has set ambitious targets for solar energy capacity, including 175 GW by 2022 and 500 GW by 2030. The government has implemented various measures to promote solar energy, such as the National Solar Mission, Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO), and Net Metering Policy.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Effective public-private partnerships are essential to meet India’s renewable energy targets. The government should promote public-private partnerships to invest in new renewable energy installations.
- Policy Recommendations: The government should implement a conducive policy structure to support the solar energy sector, including stable tariffs, long-term contracts, and a supportive regulatory environment.
Recommendations
- Education and Awareness: The government should invest in education and awareness programs to increase public understanding of solar energy and its benefits.
- Research and Development: The government should invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar technologies.
- International Collaboration: India should collaborate with other countries to share knowledge, technology, and best practices in the solar energy sector.
- Local Manufacturing: The government should promote local manufacturing of solar equipment to reduce dependence on imports and create jobs.
- Grid Integration: The government should invest in grid infrastructure to integrate solar energy into the existing power grid.
- Social and Environmental Impact: The government should consider the social and environmental impacts of solar energy projects, including land use, water resources, and biodiversity.
- Financial Incentives: The government should provide financial incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy, such as tax credits, subsidies, and low-interest loans.